ROOT: Patching the boot partition (non-US only)
On the Nokia 6300 4G and 8000 4G, you might have noticed that while ADB and DevTools allow you to install most third-party apps outside of KaiStore, you cannot install apps with ‘forbidden’ permissions such as embed-apps, embed-widget or engmode-extension (as defined by the devtools.apps.forbidden-permissions Device Preferences flag). This prevents you from sideloading and using Wallace Toolbox, telnetd, ADBroot or a bunch of BananaHackers apps, which depend on those permissions to handle app installations or gain deeper system control. If you try to install an app with any of the ‘forbidden’ permissions, WebIDE and gdeploy will throw an error:
joni@kiruria:~/dev/gdeploy$ gdeploy install ../wallace-toolbox/
GDEPLOY
-------
installationFailed: Installing apps with any of these permissions is forbidden: embed-apps,engmode-extension,embed-widgets
at /home/joni/dev/gdeploy/node_modules/node-firefox-connect/node_modules/firefox-client/lib/client-methods.js:70:19
at Client.handleMessage (/home/joni/dev/gdeploy/node_modules/node-firefox-connect/node_modules/firefox-client/lib/client.js:161:7)
at Client.readMessage (/home/joni/dev/gdeploy/node_modules/node-firefox-connect/node_modules/firefox-client/lib/client.js:220:10)
at Client.onData (/home/joni/dev/gdeploy/node_modules/node-firefox-connect/node_modules/firefox-client/lib/client.js:186:16)
at Socket.emit (events.js:314:20)
at addChunk (_stream_readable.js:297:12)
at readableAddChunk (_stream_readable.js:272:9)
at Socket.Readable.push (_stream_readable.js:213:10)
at TCP.onStreamRead (internal/stream_base_commons.js:188:23)
(Kudos to @saanaito in r/KaiOS Discord server for the console snippet!)
Most system modifications have also been blocked, and if you were to make any changes, they would be reverted upon reboot. Because in order for VoIP in WhatApp to work on newer KaiOS versions, a kernel security module called SELinux is now set to Enforcing mode. In this mode, SELinux checks for, and denies any actions, whether by the user or system, which aren’t permitted in its predefined set of rules; this includes executing any commands as root.
To root, you’ll need to edit the boot partition where SELinux resides, set it to Permissive mode, and change certain boot flags to allow system-level debugging access.
Do set aside enough time for yourself to complete this guide; it will take around 30 minutes to an hour.
Before proceeding
PROCEED AT YOUR OWN RISK AND WITH CAUTION. I provide this guide “as-is” without any guarantees or warranties. HMD does not explicitly cover software modifications under its warranty policy, so you should assume that rooting your phone will void its warranty, and you will be liable for any damages.
Proceeding with this guide will set SELinux to Permissive mode, which in turn disables voice calls in WhatsApp, and may prevent you from receiving incremental over-the-air updates. If you keep a copy of the original boot image, you can overwrite the modified partition and revert all changes, which I will cover in the last portion of the guide. But you may still permanently brick your phone if you make any mistake in the process.
It’s worth noting that in many situations, you don’t have to root your phone to remove preinstalled apps or change system settings, e.g. you can use this fork of Luxferre’s AppBuster to hide preinstalled apps from the launcher, instead of deleting them with Wallace Toolbox. You can also install CrossTweak, a Wallace Toolbox alternative which doesn’t need engmode-extension and therefore can be used on KaiOS 2.5.4 phones.
I acknowledge the risks of what I'm doing and ready to proceed
What we need
- a Nokia 6300 4G (excl. TA-1324), Nokia 8000 4G, Nokia 2720 Flip, Nokia 800 Tough or an Alcatel Go Flip 3;
- a physical computer with working Internet connection, which you have administrator privileges (setting up on a virtual machine is strongly discouraged);
- an USB cable capable of transferring data (EDL cables should also work);
- EDL programmer for your phone: 6300 4G and 8000 4G, 2720 Flip, 800 Tough or Go Flip 3 (AT&T/Cricket, T-Mobile/Metro/Rogers);
edl.pyto read and write system partitions in EDL mode:- on the 6300 4G and 8000 4G: bkerler’s EDL for macOS and Linux, bkerler’s edl-3.1 for Windows (newer versions will stuck at
main - Device detected :)); - on the 2720 Flip, 800 Tough and Go Flip 3: andybalholm’s EDL;
- Due to changes within the partition table, using andybalholm’s EDL on the 6300 4G and 8000 4G will throw an error:
AttributeError: 'gpt' object has no attribute 'partentries'. Did you mean: 'num_part_entries'? - I won’t cover QFIL or Qualcomm Product Support Tools (QPST) in this guide; if you’re more comfortable with them, you can use them as well
- on the 6300 4G and 8000 4G: bkerler’s EDL for macOS and Linux, bkerler’s edl-3.1 for Windows (newer versions will stuck at
- Python 3 and
pipforedl.pyto work; setup guide can be found for each OS below- Tip: On macOS and Linux, you can use Homebrew or your package manager of choice to set up Python, ADB,
libusband dependencies foredl.py. - Python 2.7 bundled with macOS 10.8 to 12 is NOT recommended for following this guide.
- If you don’t have an Internet connection, download and install packages manually from PyPI: pyusb, pyserial, keystone-engine, capstone, docopt, setuptools
- Tip: On macOS and Linux, you can use Homebrew or your package manager of choice to set up Python, ADB,
- Android Debug Bridge (ADB) to read the boot partition in Gerda Recovery (see Sideloading and debugging third-party applications for instructions on using ADB)
Windows users also need to download and install:
- required for the 6300 4G and 8000 4G: Gerda Recovery image file (backup) for the Nokia 8110 4G; since bkerler’s edl-3.1 cannot read from
8k.mbn, we’ll use Gerda Recovery to access ADB from Recovery mode and get the boot partition from there; - Qualcomm driver for your computer to detect the phone in EDL mode (included in bkerler’s edl-3.1 and andybalholm’s EDL under the
Driversfolder); - latest version of Zadig to configure
libusb-win32/libusb0driver; do NOT use the older version bundled inedl.pypackage as it has less chances of success
For the sake of convenience, move the MBN file and the Gerda Recovery image to the root of edl-3.1 or edl-master folder. If you need to have those in another folder, change the directory path for each command in this guide accordingly.
If you’re going the Automatic patching with 8k-boot-patcher route (only recommended for 5-6 year old computers):
- Git to clone/download the repository of the patcher tool to your computer;
- Docker Compose to provide the environment for the patcher tool to work (included in Docker Desktop)
- Windows: 2nd version of Windows Subsystem for Linux with Linux kernel update package installed (to install WSL2, turn on VT-x virtualization in BIOS, then open Command Prompt with administrative rights and type
wsl --install)
If you’re going the Manual patching with Android Image Kitchen route:
- Android Image Kitchen v3.8 (Windows, macOS/Linux)
- on Windows 10 pre-1809 and older versions of Windows: Notepad++ to edit files while preserving line endings
- (optional) Java Runtime Environment to properly sign the boot image with AVBv1
Part 1: Set up environment for EDL tools
Linux
Open a shell prompt, install Python, pip, ADB and Git from your package manager of choice, then install the dependencies for edl.py from PyPI:
- Debian/Ubuntu-based distros:
sudo apt-get install python3 python3-pip python3-venv android-sdk-platform-tools git liblzma - Fedora, CentOS, RHEL:
sudo dnf install python3 python3-pip python3-virtualenv android-tools git xz - Arch-based distros:
sudo pacman -S python python-pip3 android-tools git xz
Per PEP 668, Python 3.11 and later now enforces using virtual environments to install packages from pip. If you try to install PyPI packages with pip install at this point, it will cause an externally-managed-environment error. To install the dependencies for edl.py, create a .venv directory to host a new virtual environment, then activate it:
$ python3 -m venv .venv && source .venv/bin/activate
(env) $ pip install pyserial pypng passlib keystone-engine docopt wheel urllib3 typing-extensions pyusb pycryptodomex pycryptodome pycparser lxml idna future configparser colorama charset-normalizer certifi capstone bcrypt requests qrcode cffi pynacl cryptography paramiko Exscript setuptools
If you were following an older revision of this guide and stuck at ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'distutils', starting with Python 3.12, distutils, which is a dependency of capstone, has been deprecated and removed (see Python documentation page What’s New In Python 3.10). It’s now superceded by the third-party package setuptools, which you can install from PyPI with pip install setuptools.
If you have any problems seeing your phone on Debian/Ubuntu-based distros, append blacklist qcserial in /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf, and copy 51-edl.rules and 50-android.rules from the Drivers folder (root of EDL directory if you have andybalholm’s EDL) to /etc/udev/rules.d:
# echo "blacklist qcserial" > /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf
# cp Drivers/51-edl.rules Drivers/50-android.rules /etc/udev/rules.d
On some Linux distributions, you may need to temporarily disable ModemManager before connecting your phone. ModemManager is a tool which handles mobile broadband connections; when you connect your phone in EDL mode, it’ll identify the phone as a Qualcomm modem and try to configure the device, which might interfere with edl.py. If you’re using a Linux distro with systemd, ModemManager can be stopped by:
# systemctl stop ModemManager.service
Switch your phone to EDL mode and connect it to your computer. Either:
- if your phone is on, dial
*#*#33284#*#*to turn on debugging mode, connect it to your computer and typeadb reboot edlin the shell prompt. - if your phone is off, press and hold
*and#at the same time while inserting the USB cable to the phone.
In both cases, the screen should flash an ‘enabled by KaiOS’ logo and become blank. This is normal behaviour letting you know you’re in EDL mode and can proceed.
macOS
Follow the instructions to install Homebrew on its homepage, install Android SDK Platform Tools package, latest Python, libusb and dependencies for edl.py from PyPI. Basically open Terminal and copy-paste each line of this code, and type your password when prompted:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
brew install python android-platform-tools libusb
python3 -m venv env
source env/bin/activate
python3 -m pip install pyusb pyserial capstone keystone-engine docopt setuptools
python3 -m pip install setuptools
python3 -m pip install --pre --no-binary capstone capstone
Switch your phone to EDL mode and connect it to your computer. Either:
- if your phone is on, dial
*#*#33284#*#*to turn on debugging mode, connect it to your computer and typeadb reboot edlin Terminal. - if your phone is off, press and hold
*and#at the same time while inserting the USB cable to the phone.
In both cases, the screen should blink with an ‘enabled by KaiOS’ logo then become blank. This is normal behaviour letting you know you’re in EDL mode and can proceed.
Windows
- Head over to Python’s official download page for Windows and download the correct installer for your architecture (if you’re in doubt select amd64/x86_64), or download the latest version of Python from Microsoft Store. If you’re downloading from Microsoft Store, skip to step 4.
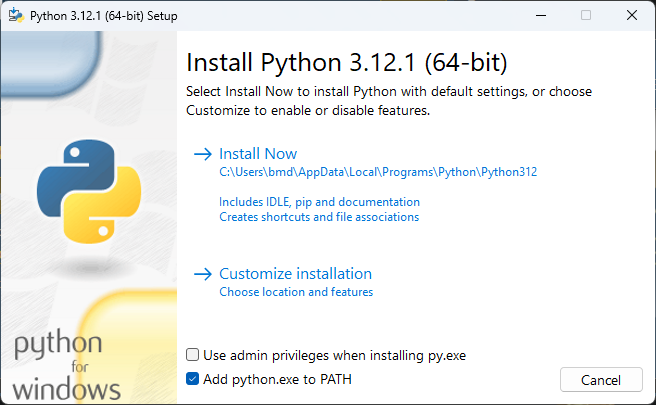
- Proceed with installing Python as usual. If you choose to customise your installation, include
pipand tick Add Python to environment variables. Don’t forget to tick the box next to “Add python.exe to PATH” to add Python as a global environment variable, otherwise you’ll have a hard time using Python to run scripts later on.
- On Windows 10/11, typing
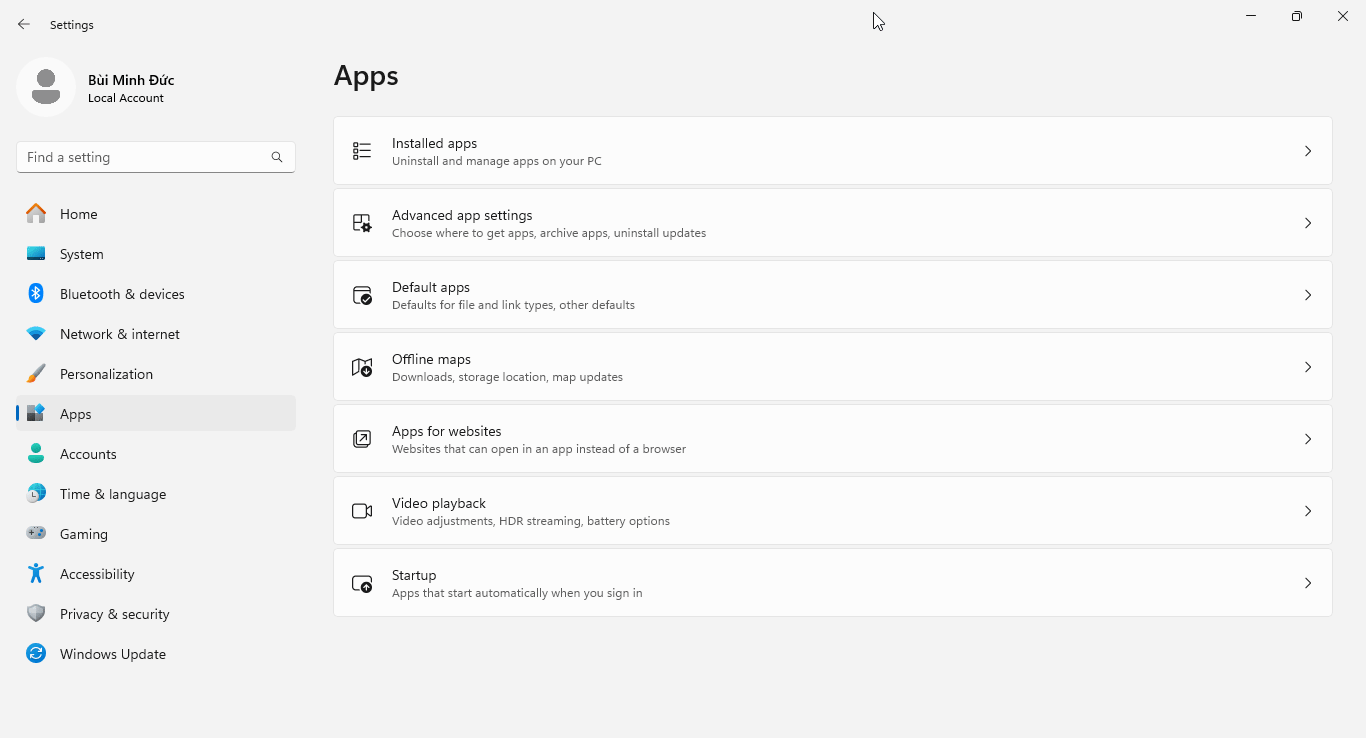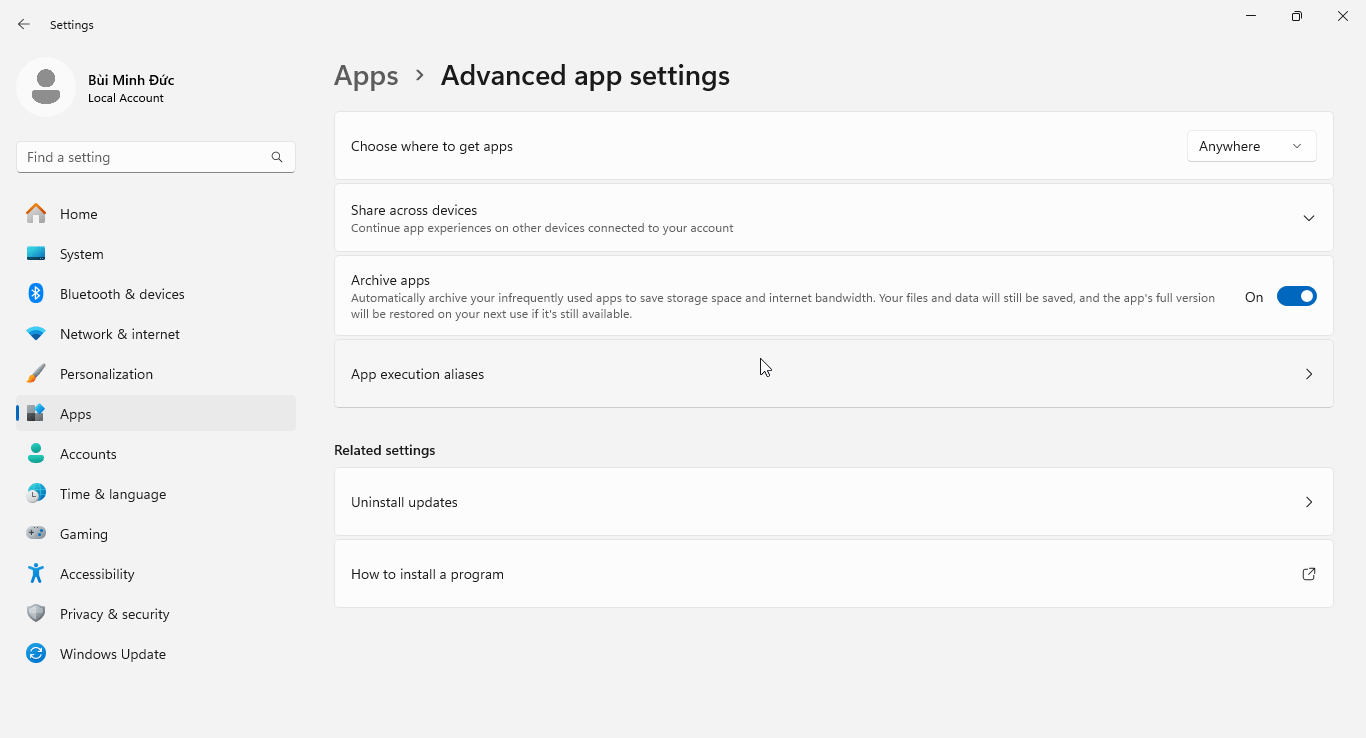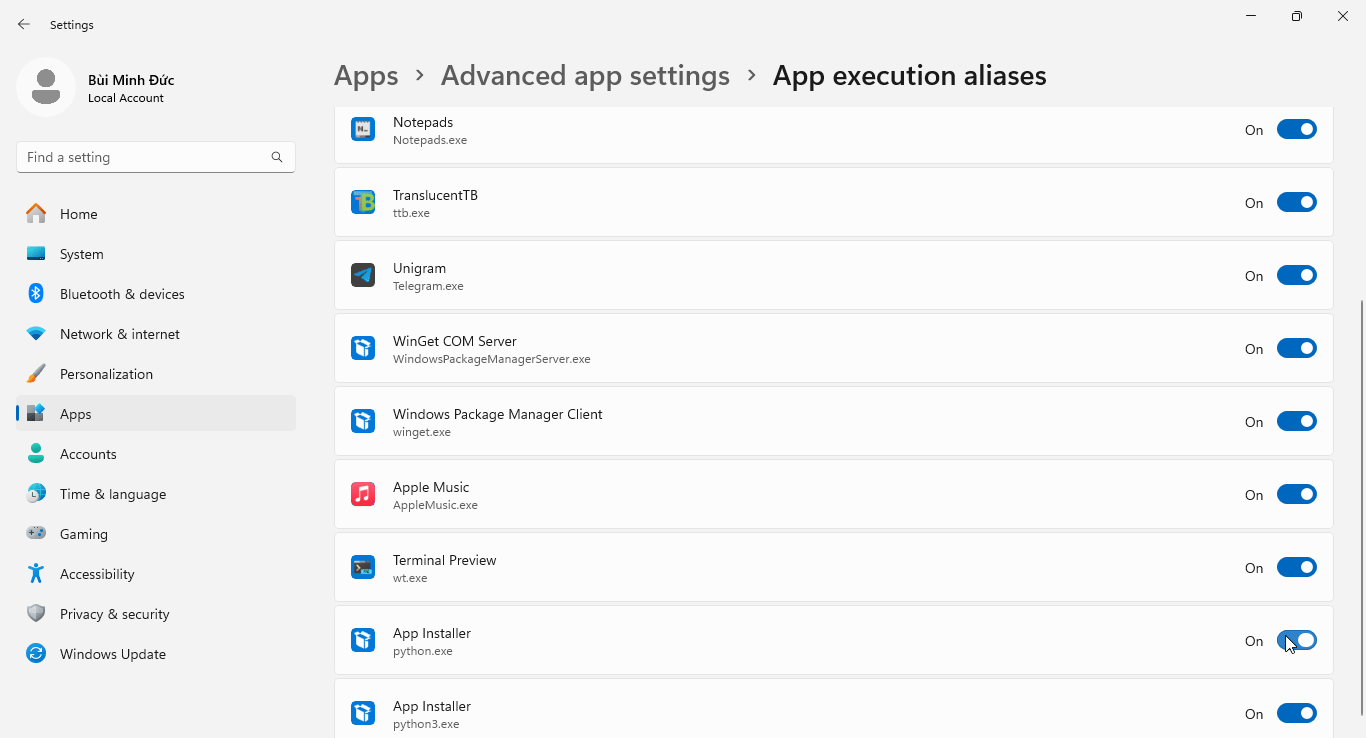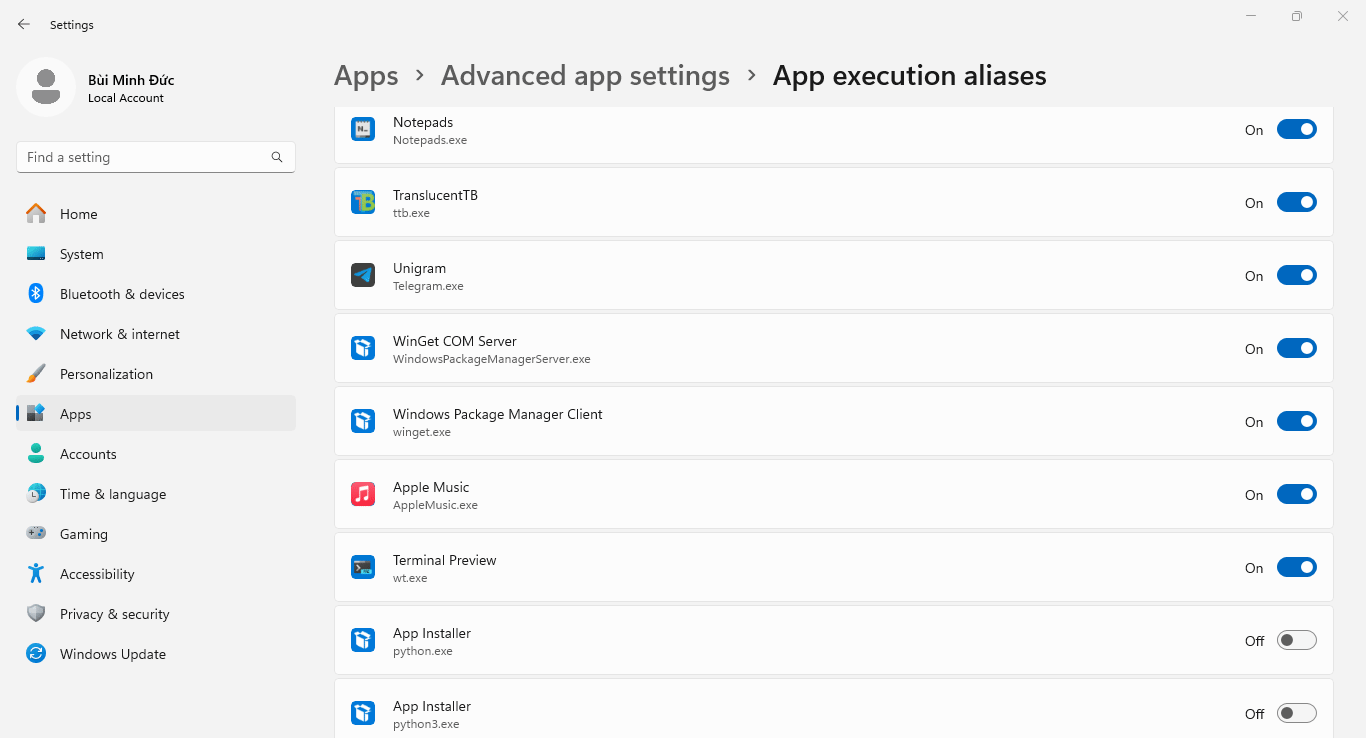
pythonorpython3within Command Prompt/Windows Terminal will run the Microsoft Store version of Python. To override this default into running the locally installed version, toggle off App Installer (python.exe) and App Installer (python3.exe) under:- Windows 10: Settings → Apps → Apps & features → App execution aliases
- Windows 11: Settings → Apps → Advanced app settings → App execution aliases
- Open Command Prompt/Windows Terminal with administrator rights and install the dependencies for
edl.pyfrom PyPI:
pip3 install pyusb pyserial capstone keystone-engine docopt setuptools
- Extract the previously downloaded
edl.pypackage, open Drivers, Windows and runQualcomm_Diag_QD_Loader_2016_driver.exewith administrator rights. Proceed with installation and leave everything as default, restart the computer if it prompts you to do so.
- Switch your phone to EDL mode and connect it to your computer. Either:
- if your phone is on, dial
*#*#33284#*#*to turn on debugging mode, connect it to your computer and typeadb reboot edlin Command Prompt/Windows Terminal. - if your phone is off, press and hold
*and#at the same time while inserting the USB cable to the phone.
- if your phone is on, dial
In both cases, the screen should blink with an ‘enabled by KaiOS’ logo then become blank. This is normal behaviour letting you know you’re in EDL mode and can proceed.
- To replace the installed
qcusbserdriver withlibusb-win32for use withedl.py, download and open Zadig (do NOT use the version included in the EDL package). Tick Options, List All Devices and selectQHSUSB__BULK(your device in EDL mode) in the main dropdown menu. In the target driver box, which the green arrow is pointing to, click the up/down arrows until you seelibusb-win32 (v1.2.7.3)orlibusb0 (v1.2.5.0), then click Replace Driver.
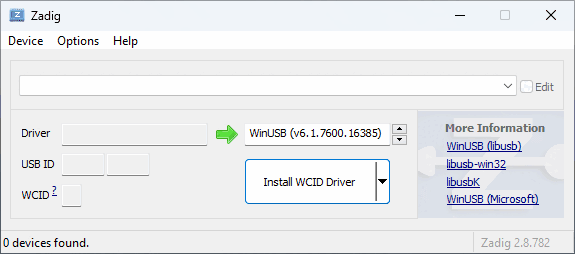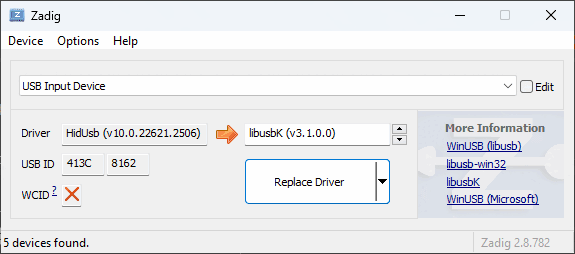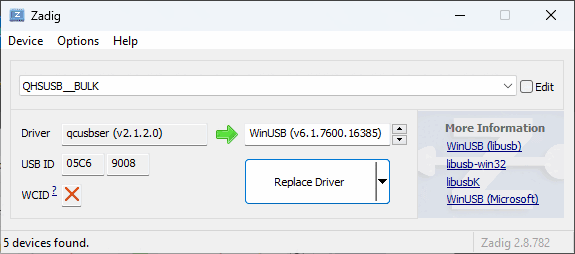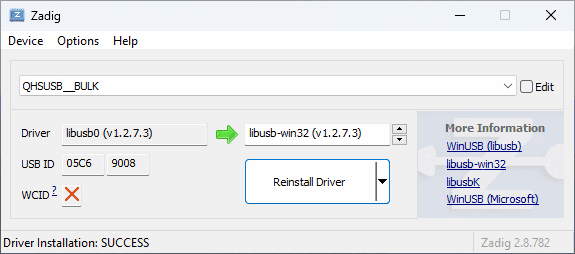
[!NOTE] Windows will automatically create restore points on driver installation, as Zadig suggests in its tooltips. On older computers, this might cause issues with driver configuration process being lengthened past the 5-minute mark. If Zadig aborts the process and hangs, kill Zadig with Task Manager, remove and re-insert the battery on the phone to exit and re-enter EDL mode, then try to install again. (seems to be improved with Zadig 2.9)
- If you’re configuring the driver for the first time, an “USB Device Not Recognised” pop-up may appear. Exit EDL mode by removing and re-inserting the battery, then turn on the phone in EDL mode again.
Part 2: Obtaining the boot partition
Nokia 8000 4G and Nokia 6300 4G with bkerler’s EDL
Beware: due to the firehose loader being malfunctioned,
edl.pyonly accepts one command each session, after which you’ll have to disconnect the phone and restart the phone in EDL mode. If you try to execute a second command, it will result in abytearray index out of rangeerror.
-
Turn on the phone in EDL mode.
-
Open the extracted EDL folder in Command Prompt/Terminal. Flash the Gerda Recovery image to the recovery partition by typing:
python edl.py w recovery recovery-8110.img --loader=8k.mbn
If the progress bar stops at 99% (not earlier) and you get error 'usb.core.USBError: [Errno None] b'libusb0-dll:err [_usb_reap_async] timeout error\n' or usb.core.USBError: [Errno 60] Command timed out, don’t mind the error and proceed with the next step.
-
When finished, disconnect the phone from your computer and exit EDL mode by removing and re-inserting the battery.
-
Then, hold down the top Power button and * to turn the phone on in recovery mode. Connect the phone to your computer again.
[!WARNING] Be careful not to boot into system at this point! While SELinux is still in
Enforcedmode, it will try to run/system/bin/install-recovery.shand revert all system modifications on boot, in this case, the custom recovery image we’ve just flashed will be overwritten by the stock one. If you accidentally start into normal mode (with the usual Nokia chime), you’ll have to start over from step 1.
Don’t worry if this boots into a white screen: this is because the display driver for the Nokia 8110 4G included in the recovery image are not compatible with the display of 8000 4G/6300 4G. Check if ADB can recognise the phone by typing adb devices into Command Prompt/Terminal.
- Navigate the shell prompt to the extracted
platform-toolsfolder withcd(if needed). Pull the boot partition from the phone to your computer with ADB:
adb pull /dev/block/bootdevice/by-name/boot boot.img
You should now see /dev/block/bootdevice/by-name/boot: 1 file pulled, 0 skipped. and have a copy of the boot partition with the size of 32.0 MB (32,768 KB). Fetched boot image will be saved to the current directory.
- Reboot the phone into normal mode by typing
adb rebootinto Command Prompt/Terminal, or remove and re-insert the battery. Our custom Gerda Recovery partition will now be overwritten by the default one.
Feel free to disconnect the phone from your computer for now.
Nokia 2720 Flip and Nokia 800 Tough with andybalholm’s EDL
Unlike that of the 6300 4G and 8000 4G, our phones’ EDL programmer properly reads and writes from the phone, so the steps are more straightforward.
- Switch your phone to EDL mode and connect it to your computer. Either:
- if your phone is on, dial
*#*#33284#*#*to turn on debugging mode, connect it to your computer and typeadb reboot edlin Command Prompt/Terminal; - if your phone is off, hold down both volume keys on the side (2720 Flip) or both D-Pad Up and Down keys (800 Tough) at the same time while inserting the USB cable to the phone.
- if your phone is on, dial
In both cases, the screen should blink with an ‘Powered by KaiOS’ logo then go blank. This is normal behaviour letting you know you’re in EDL mode and can proceed.
- Extract the EDL package and open the folder in Command Prompt/Terminal. Pull the boot partition of the phone to the current directory on your computer by typing either of these commands, depending on which phone you have:
python edl.py -r boot boot.img -loader 2720.mbn
python edl.py -r boot boot.img -loader 800t.mbn
- When finished, reboot the phone into normal mode by typing
python edl.py -resetinto Command Prompt/Terminal, or remove and re-insert the battery.
You should now have a copy of the boot partition with the size of 25.0 MB (25,600 KB). Feel free to disconnect the phone from your computer for now.
[!WARNING] Copy and keep the original boot partition somewhere safe in case you need to restore the phone to the original state to do over-the-air updates or re-enable WhatsApp calls.
Part 3: Patching the boot partition
Automatic patching with 8k-boot-patcher
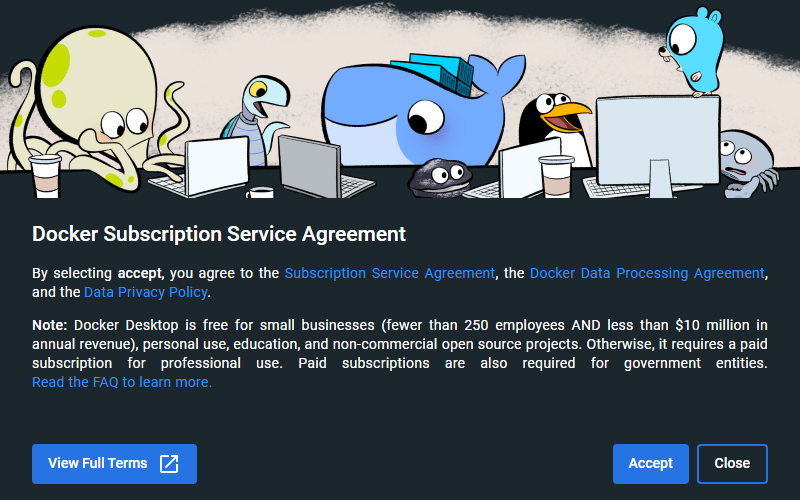
- Download and install Docker Desktop. Once set up, open the program, click Accept on this box and let the Docker Engine start before exiting.
- Use Git to clone/download the boot patcher toolkit by typing this into Command Prompt/Terminal. This will download the toolkit and have Docker set it up. Do not omit the dot/period at the end of this command, this tells Docker where our downloaded toolkit are located on the system.
git clone https://gitlab.com/suborg/8k-boot-patcher.git && cd 8k-boot-patcher && docker build -t 8kbootpatcher .
- Copy the
boot.imgfile you just pulled from your phone to the desktop and do NOT change its name. Type this into Command Prompt/Terminal to run the patching process:- Windows:
docker run --rm -it -v %cd%/Desktop:/image 8kbootpatcher - macOS/Linux:
docker run --rm -it -v ~/Desktop:/image 8kbootpatcher
- Windows:
$ docker run --rm -it -v ~/Desktop:/image 8kbootpatcher
Boot image found, patching...
writing boot image config in bootimg.cfg
extracting kernel in zImage
extracting ramdisk in initrd.img
charger
data
[...]
ueventd.qcom.rc
ueventd.rc
verity_key
4037 blocks
4979 blocks
reading config file bootimg.cfg
reading ramdisk from myinitrd.img
Writing Boot Image boot.img
Boot image patched!
That’s it! On your desktop there will be two new image files, the modified boot.img and the original boot-orig.img. You can now head to part 4.
Manual patching with Android Image Kitchen
- Extract the Android Image Kitchen package and copy the boot image you just pulled over to the root of the extracted folder.
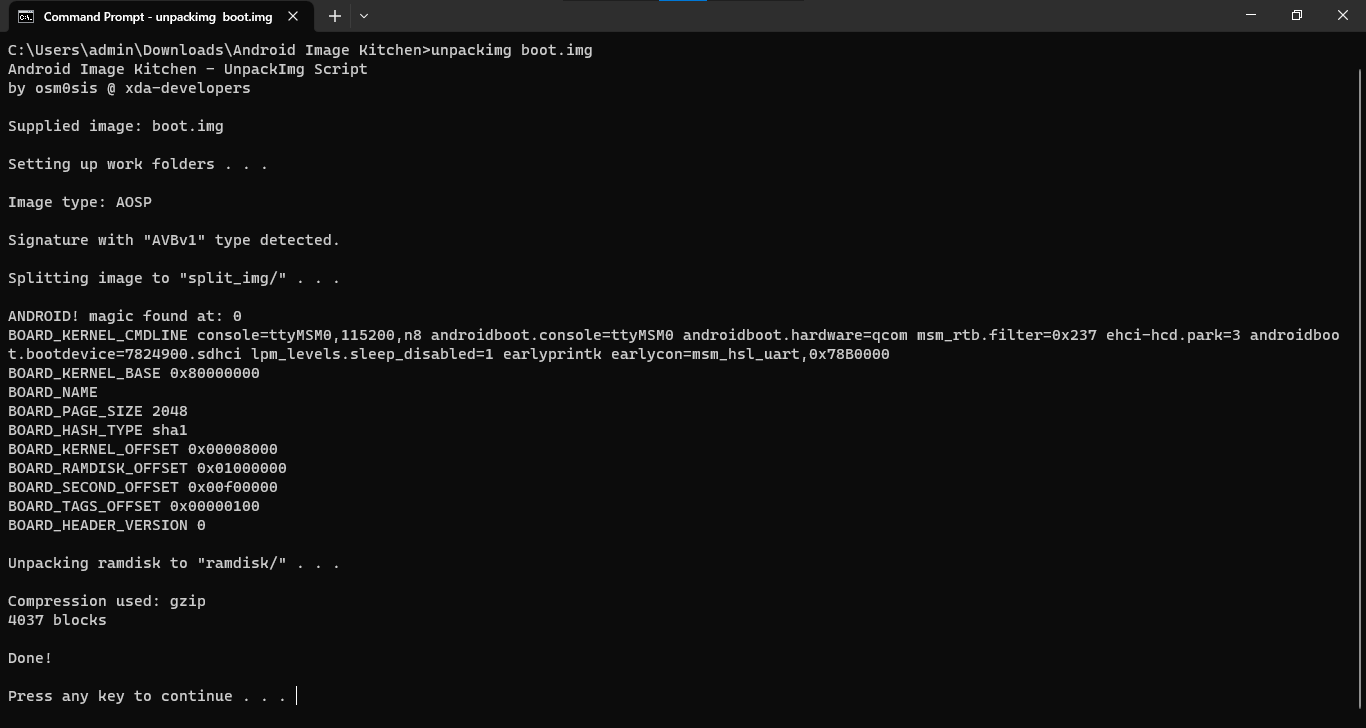
- Open the folder in Command Prompt/Terminal and type
unpackimg boot.img. This will split the image file and unpack the ramdisk to their subdirectories.
[!WARNING] Be sure to edit the files correctly, else the phone won’t boot!
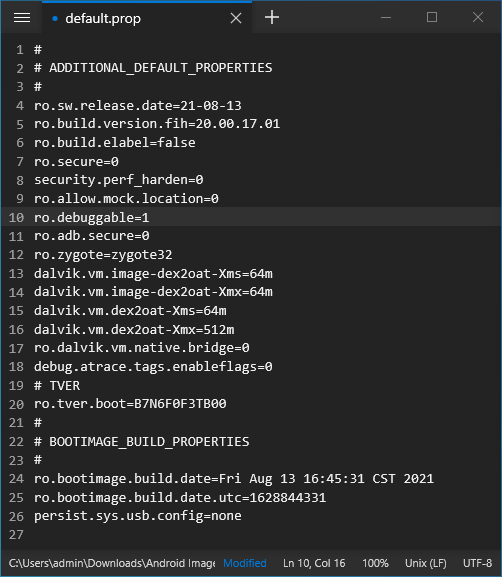
- Let the editing begin! First, open
ramdisk/default.propusing Notepad++ and change:- line 7:
ro.secure=1→ro.secure=0 - line 8:
security.perf_harden=1→security.perf_harden=0 - line 10:
ro.debuggable=0→ro.debuggable=1
- line 7:
@@ -4,9 +4,9 @@
ro.sw.release.date=21-08-13
ro.build.version.fih=20.00.17.01
ro.build.elabel=false
- ro.secure=1
- security.perf_harden=1
+ ro.secure=0
+ security.perf_harden=0
ro.allow.mock.location=0
- ro.debuggable=0
+ ro.debuggable=1
ro.adb.secure=0
ro.zygote=zygote32
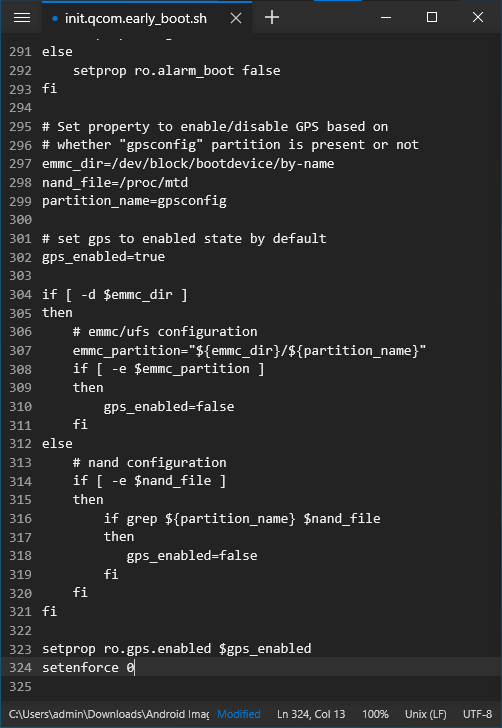
- Open
ramdisk/init.qcom.early_boot.shin Notepad++ and addsetenforce 0as a new line at the end of the file.
@@ -312,14 +312,14 @@
else
# nand configuration
if [ -e $nand_file ]
then
if grep ${partition_name} $nand_file
then
gps_enabled=false
fi
fi
fi
setprop ro.gps.enabled $gps_enabled
+ setenforce 0
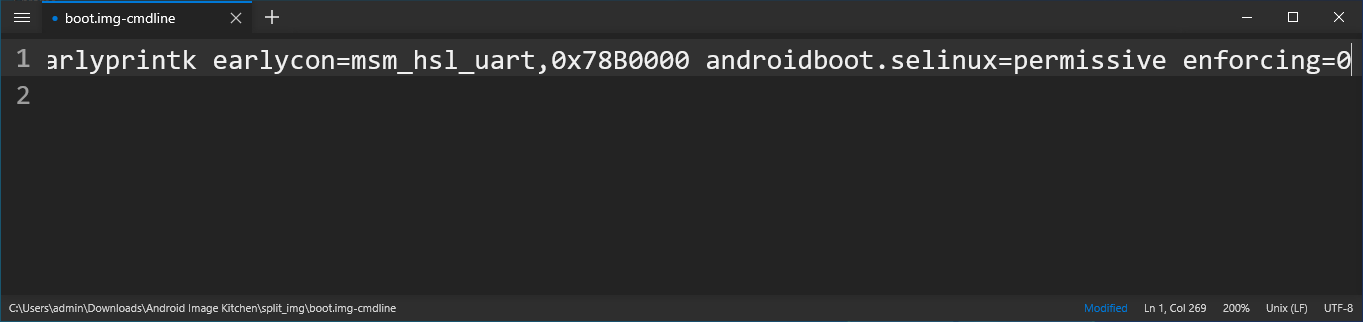
- Go back to the Android Image Kitchen folder and open
split_img/boot.img-cmdlinein Notepad++. Without adding a new line, scroll to the end of the first line and appendandroidboot.selinux=permissive enforcing=0.
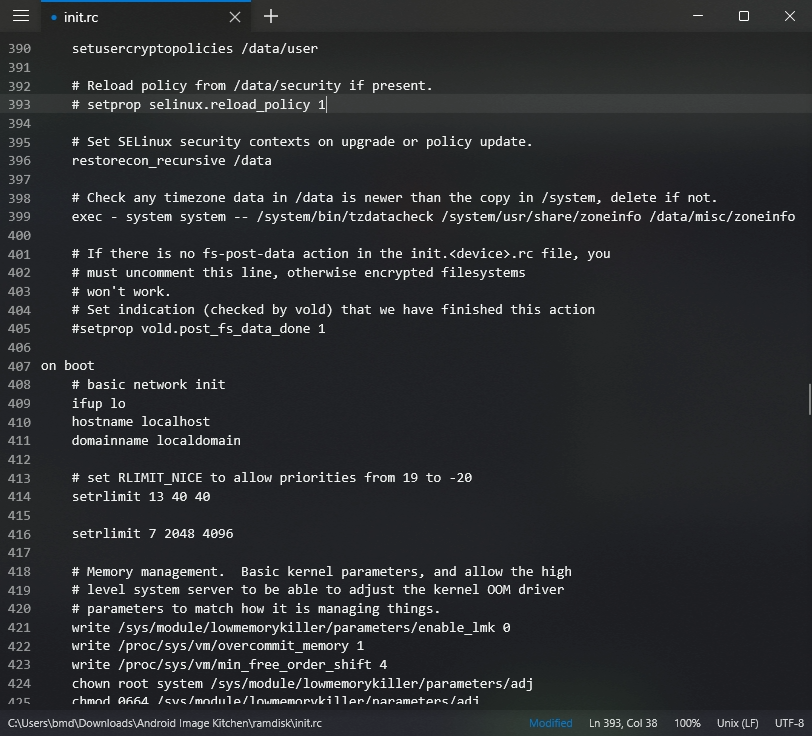
- Open
ramdisk/init.rc(NOTramdisk/init) and delete line 393setprop selinux.reload_policy 1or mark a comment as shown. This will ultimately prevent SELinux from overwriting the policy changes we made above.
If you want to know why I put an additional line to set /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/enable_lmk to 0, see [Expanding RAM with swapfile].
@@ -390,7 +390,6 @@
setusercryptopolicies /data/user
# Reload policy from /data/security if present.
- setprop selinux.reload_policy 1
# Set SELinux security contexts on upgrade or policy update.
restorecon_recursive /data
@@ -418,9 +418,10 @@
# Memory management. Basic kernel parameters, and allow the high
# level system server to be able to adjust the kernel OOM driver
# parameters to match how it is managing things.
+ write /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/enable_lmk 0
write /proc/sys/vm/overcommit_memory 1
write /proc/sys/vm/min_free_order_shift 4
chown root system /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/adj
chmod 0664 /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/adj
chown root system /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree
chmod 0664 /sys/module/lowmemorykiller/parameters/minfree
- And that’s a wrap! Open the Android Image Kitchen folder in Command Prompt/Terminal and type
repackimgto package your modified boot partition.
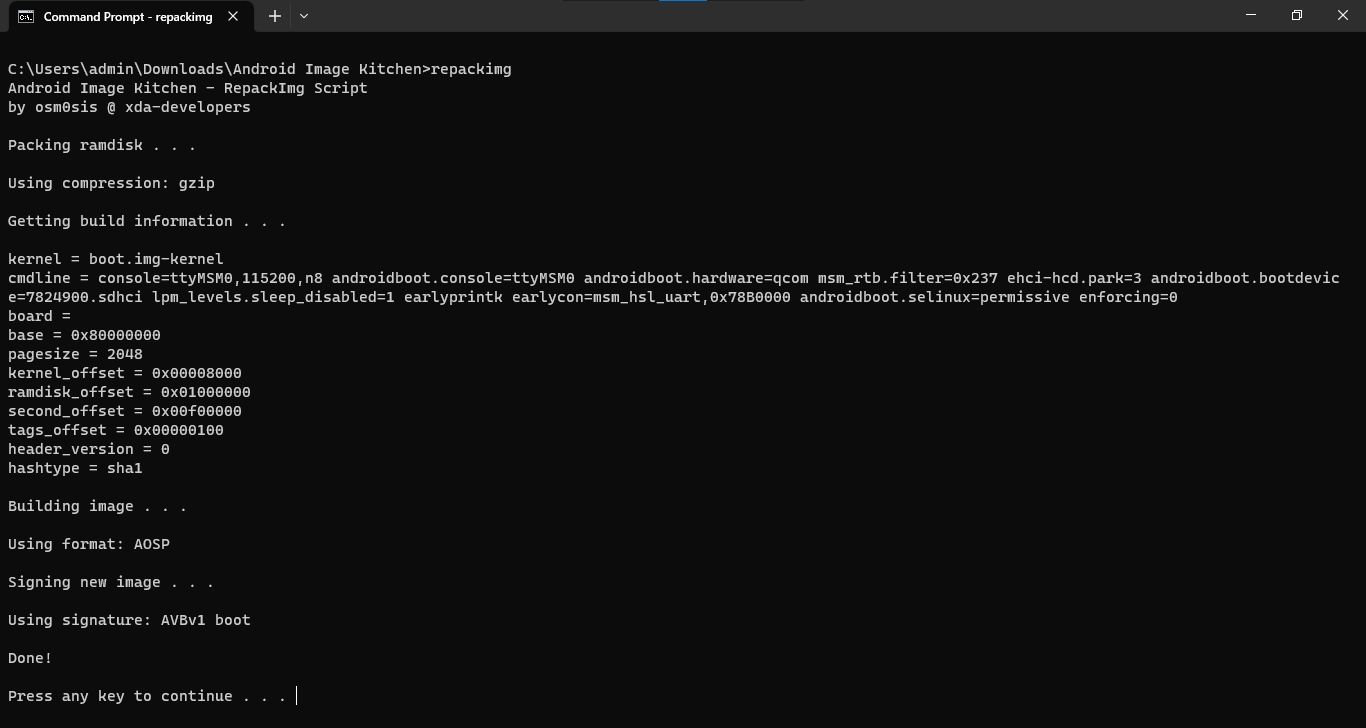
If you happen to encounter an error during the signing process, that’s likely because the process uses java to power the boot-signer.jar sequence and you don’t have it installed. The image will still be packaged and ready for flashing, but if you’re a perfectionist, you can install JRE and try again.
If the new image is barely over 1/3 the size of the original image, it’s normal and you can proceed.
Part 4: Flashing the modified boot partition
-
Turn on your phone in EDL mode and connect it to your computer.
-
Move the newly created
boot.img,unsigned-new.imgorimage-new.imgto the EDL folder and open Command Prompt/Terminal within it. From here type either of these commands depending on which image file you have:
python edl.py w boot boot.img --loader=8k.mbn
python edl.py w boot unsigned-new.img --loader=8k.mbn
python edl.py w boot image-new.img --loader=8k.mbn
For Nokia 2720 Flip and Nokia 800 Tough with andybalholm’s EDL:
python edl.py -w boot boot.img -loader 2720.mbn
python edl.py -w boot boot.img -loader 800t.mbn
Again, if the progress bar stops at 99% and you get a timeout error, this is because the programmer doesn’t send any information back to edl.py when the image has been successfully written. Don’t mind the error and go on with the next step.
- Restart the phone to normal mode by typing
python edl.py reset. And we’re done!
Next steps
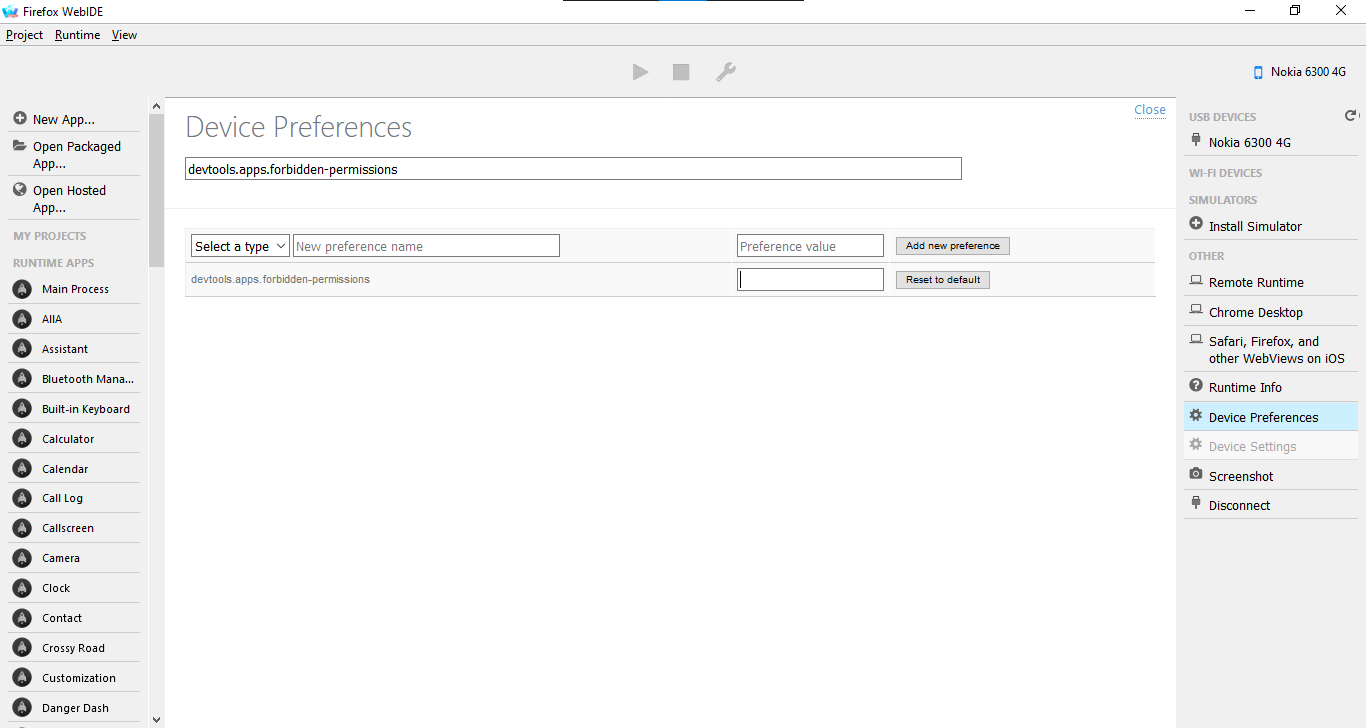
- Now that you’ve rooted your phone, to install apps with ‘forbidden’ permissions, connect your phone to a WebIDE session, open Device Preferences in the right pane, clear the value of
devtools.apps.forbidden-permissions, then restart B2G by either reboot the phone or hold the top Power button and select Memory Cleaner, Deep Clean Memory.
- If you wish to retain privileged permissions after restoring the phone to its unrooted state, before doing so, back up all data, sideload Luxferre’s CrossTweak then press # to perform a privileged factory reset; this will wipe all data of the phone and let you set up with a privileged user session. This session will last until an OTA update overrides or you choose to factory reset the phone.
- (Proof-of-concept, does NOT work) After rooting, you can spoof SELinux’s Enforced status for VoIP in WhatsApp by typing these commands one-by-one into the rooted ADB shell. This will last until a restart.
echo -n 1 > /data/enforce
mount -o bind /data/enforce /sys/fs/selinux/enforce
If you wish to revert all changes you’ve made, connect your phone to the computer in EDL mode, move the original boot image file to edl-3.1 or edl-master folder, open Command Prompt/Terminal and type:
python edl.py w boot boot.img --loader=8k.mbn
python edl.py reset